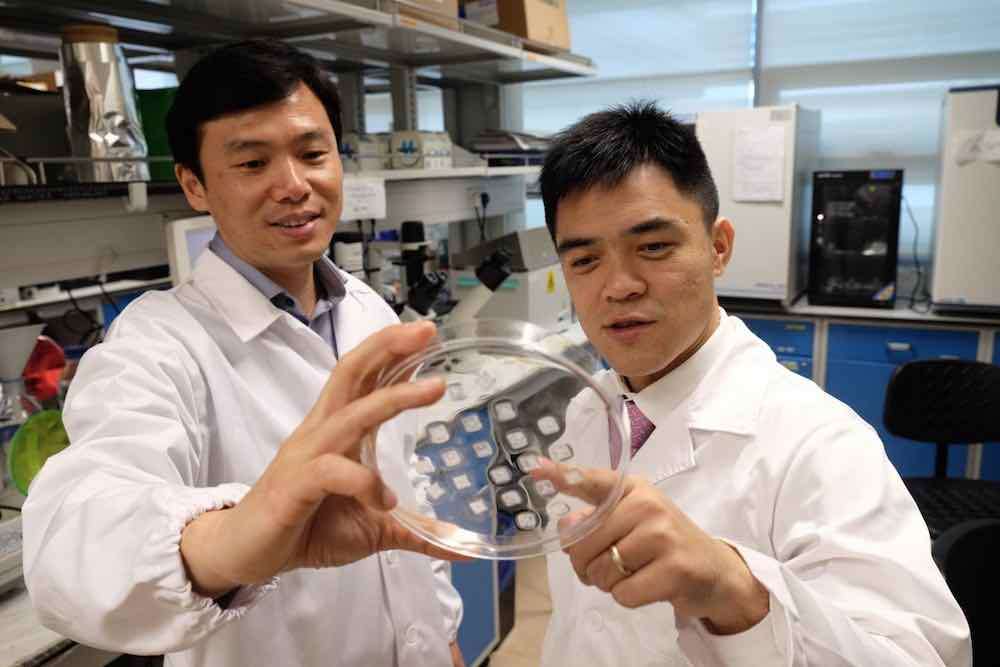
MIT is Developing Color-Changing Tattoos that Can Monitor Your Diabetes in Real Time
Instead of using traditional ink, these researchers are using biosensors to monitor the body's glucose, sodium, and alkali levels.
Instead of using traditional ink, these researchers are using biosensors to monitor the body's glucose, sodium, and alkali levels.
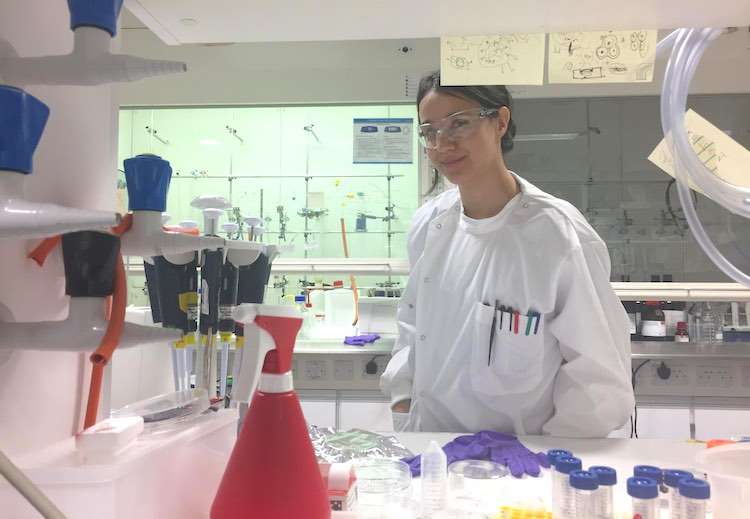

This 24-year-old Colombian native has just developed a revolutionary breakthrough in restoring vision to the blind.

Up until now, it has been impossible for enamel to regenerate on a patient's tooth – but this new study means that tooth decay may be a thing of the past.
The process, which mimics the natural one occurring in babies, and uses "a person's own body fats to burn more energy," produced 30% fat loss.

With proper funding, the team believes they could be growing lungs for transplant patients much sooner than expected.
A new update from this research organization says that human trials for an implantable bioartificial kidney could be on the horizon.
A team of researchers has discovered that there may be more truth to Irish folklore than scientists give it credit for.
Hidden in the wilderness of Yellowstone National Park is a special kind of bacteria that sucks up pollutants and transforms it into electricity.
This mobile bioprinter could soon be used to print out a patient's own skin tissue in order to heal wounds and burns.
These specially-trained canines are being hired to protect both humans and bears thanks to their special genetic skillset.
Researchers have made a major breakthrough in developing a cure for type 1 diabetes - and human trials are set to begin soon.
Researchers have discovered a way to make mosquitos feel more satisfied - and it could prevent thousands of infections around the world.
This rare material was brought to Earth by the massive asteroid that wiped out the dinosaurs 66 millions years ago – and now, it could cure cancer.
This brand new houseplant goes one step beyond air filters by cleansing the air of common chemicals such as benzene, chloroform, and formaldehyde.
Not only could the discovery spell the end of aged skin, it could also serve as a stepping stone to defeating several common diseases and infections.
Scientists have discovered a gene that makes people happy, but it is said to work only in women. The findings could help explain why women are often happier than men, the team of US researchers said. The study focused on a gene called MAOA that affects the levels of feel-good chemicals in the brain. Dr. Henian Chen said its effects could be cancelled out by testosterone.
According to Dr. Marc Bekoff Ph.D., emotions like joy, love, empathy, compassion, kindness, and grief can readily be shared by improbable friends including predators and prey such as a cat and a bird, a snake and a hamster, and a lioness and a baby oryx.
Marine biologists were taking a swim through the Solomon Islands when an eerily glowing turtle floated through the coral.
Recent Stories
A Heartfelt Reminder to Appreciate the Ones We Love
Cherish the Woman Who Stands by You
Breaking Generational Cycles of Pain
Living by Your Own Values, Not Others' Approval
When Life Brings Rain, It’s Okay to Rest
Before You Judge Someone's Life, Take a Moment to Walk in Their Shoes.
A Friend Who Spreads Gossip is Not a True Friend at All
The Value of Human Connection Over Digital Convenience
The Quiet Kind of Love
One Day, Your Mom Won’t Call You Anymore
I’ve reached a point in my life...
Happiness is a mindset, a conscious choice we make every day