Scientists Discover Brain Circuit Linked to Food Impulsivity-And It Could Lead to New Treatments for Overeating
Researchers found that activating a specific neural pathway in the brain can amplify or reduce impulsive eating, regardless of the foods.
From zeroing in on different cancer cures to restoring vision and hearing to the blind and deaf—2019 was a year filled with medical breakthroughs.
While some of these accomplishments may be varied in their stages of research, each notable study is just one more milestone towards treating some of humanity's most debilitating conditions.
So without any further ado, let's give it up for the top ten health and medical breakthroughs of 2019.
An exciting study that was published back in January found that exposure to blue light is an effective, non-pharmaceutical treatment for high blood pressure, which simultaneously reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
The researchers who conducted the study from the University of Surrey and Heinrich Heine University Duesseldorf discovered that exposure to whole-body blue light significantly reduced the systolic blood pressure of participants by almost 8 mmHg, compared to the control light which had no impact.
What's even more remarkable is that the reduction of blood pressure from blue light is similar to what is seen in clinical trials with blood pressure lowering drugs.
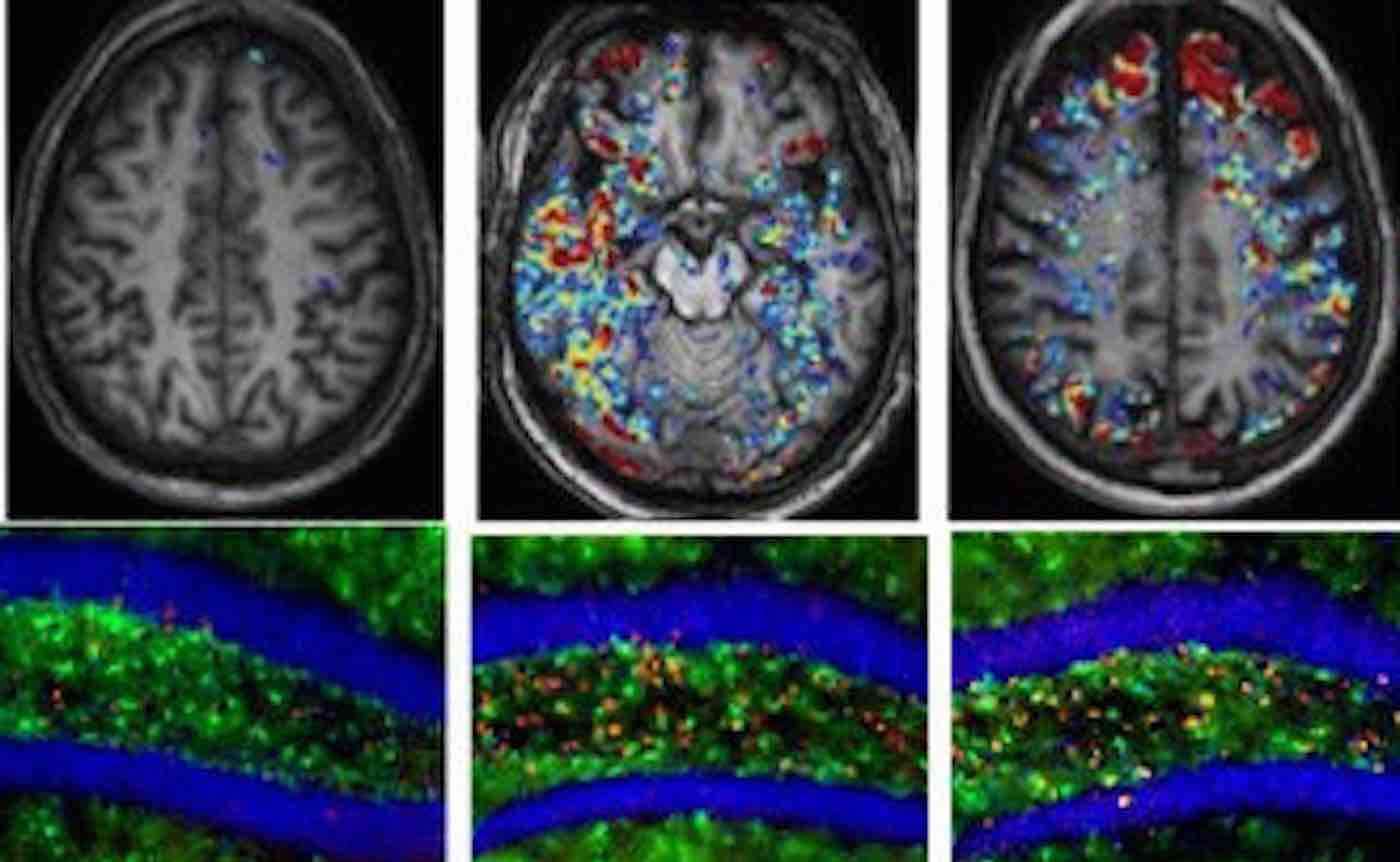
Rather than targeting the typical rogue proteins associated with dementia, scientists found earlier this month that—for the very first time—they have reversed dementia in mice with a drug that reduces inflammation.
Up until now, most dementia treatments have targeted the amyloid plaques that are found in people with Alzheimer's disease. However, experiments conducted at the University of California, Berkeley suggest targeting inflammation in the brain might stop it in its tracks.

If you didn't already have enough reason to eat your vegetables, this study published back in May says that broccoli contains an amazing ingredient which could be the "Achilles' heel" of cancer.
Broccoli is part of the cruciferous vegetable family, which includes cauliflower, cabbage, kale and Brussels sprouts—and though many people don't like their taste, these vegetables contain a tiny, but powerful molecule that deactivates the gene responsible for cancerous tumor growth, known as WWP1.
Millions of blind people could have their vision restored using stem cells taken from the eyes of non-living donors, according to Scottish research publish back in March.
Thanks to the pioneering tissue transplant, eight patients with a common condition that destroys vision had the affected area repaired—and two patients were even able to read again after having severe macular degeneration.
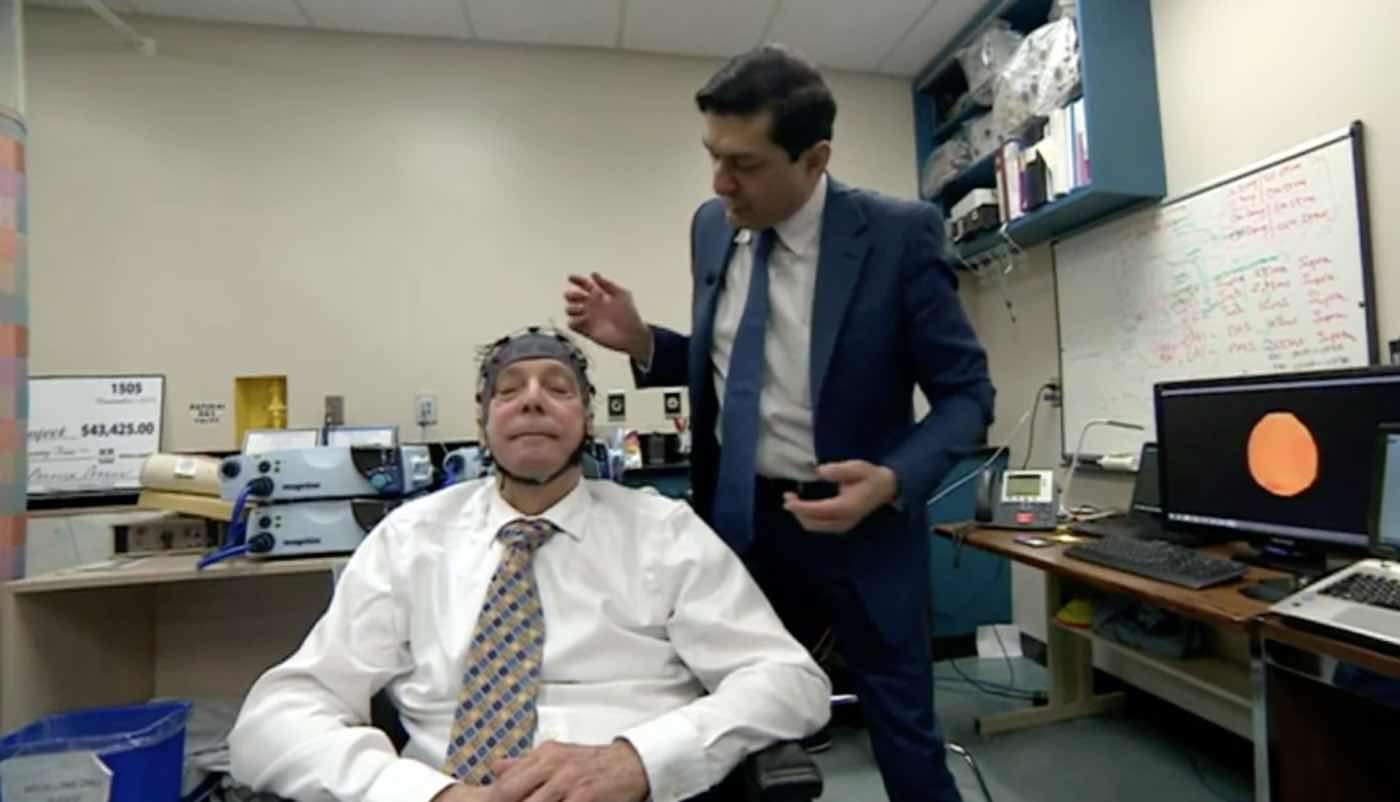
Back in April, Canadian researchers developed a new treatment for mobility-impaired Parkinson's disease patients—and the results were "beyond their wildest dreams."
Scientists from Western University in Ontario published the results of a pilot study in which they used spinal implants to improve motor function in several patients with advanced Parkinson's.
Prior to the study, the patients were barely able to stand on their own without falling over or they were forced to depend entirely on wheelchairs for mobility. After getting the spinal implant, however, the patients are now capable of walking unassisted for the first time in years.
According to a report from May, people who experience anxiety symptoms might be helped by taking steps to regulate the microorganisms in their gut using probiotic and non-probiotic food and supplements.
Anxiety symptoms are common in people with mental diseases and a variety of physical disorders, especially in disorders that are related to stress. Previous studies have shown that as many as a third of people will be affected by anxiety symptoms during their lifetime.
Increasingly, research has indicated that gut microbiota—the trillions of microorganisms in the gut which perform important functions in the immune system and metabolism by providing essential inflammatory mediators, nutrients and vitamins—can help regulate brain function through something called the "gut-brain axis."

In August, researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine may have found the key to restoring hearing in people with irreversible deafness.
Using genetic tools in mice, researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine say they identified a pair of proteins that precisely control when sound-detecting cells, known as hair cells, are born in the mammalian inner ear.
"Scientists in our field have long been looking for the molecular signals that trigger the formation of the hair cells that sense and transmit sound," says Dr. Angelika Doetzlhofer, associate professor of neuroscience at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. "These hair cells are a major player in hearing loss, and knowing more about how they develop will help us figure out ways to replace hair cells that are damaged."

As MDMA is now being recognized as a groundbreaking cure for emotional trauma, a new clinic in Pennsylvania could become one of the first legally-sanctioned facilities for using the psychoactive drug on treatment-resistant PTSD in the United States.
Now that it has reportedly opened its doors in Wyndmoore, The Landing medical facility will specialize in using several psychoactive drugs to treat a variety of mental health disorders.
Particularly, it has been pushing to receive FDA approval on using MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for patients whose Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder has been untreatable.

Dental fillings may soon be a thing of the past, thanks to this breakthrough from Chinese scientists.
Enamel is the mineralized substance that protects the surface of teeth. Though it is one of the toughest tissues in our bodies, it is prone to degradation over time particularly as a result of consistent exposure to certain acids that are found in food and drinks.
We currently use resins and ceramics to fill in deteriorated enamel, but these fillings can often become loose within just a few years of their placement—and with tooth decay being one of the most prevalent chronic diseases amongst humans, scientists have puzzled over how they can recreate enamel.
Until now, we have not been able to reproduce the toughened tissue because of its complex cellular structure—but back in September, a team of researchers from Zhejiang University School of Medicine developed a gel that makes enamel repair itself.
With pancreatic cancer ranking as one of the most deadly forms of cancer, researchers were excited to report on a promising new breakthrough for a treatment.
Pancreatic cancer, which maintains a 95% mortality rate, is resistant to all current treatments. Patients have extremely poor chances of surviving for five years after being diagnosed—and since the disease does not show symptoms until the advanced stages, it is notoriously hard to diagnose.
However, this Tel Aviv University study published earlier this month finds that a small molecule has the ability to induce the self-destruction of pancreatic cancer cells. The research was conducted with xenografts—transplantations of human pancreatic cancer into immunocompromised mice. The treatment reduced the number of cancer cells by 90% in the developed tumors a month after being administered.
Cure Your Friends Of Negativity By Sharing The Good News To Social Media…
Be the first to comment